Finite State Automation (DFA) Contains With |Examples|
Rajkumar Lama
July 18, 2019
Descrete Structure
,
DFA contains with
,
dfa examples
,
Discrete Structure
,
DS
,
DS Notes
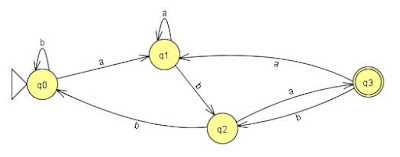
1. Construct finite state automata (DFA) that contains with abb
Solution :
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with ab
q3 = string with abb
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with ab
q3 = string with abb
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
| f | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | ||
| ε | q0 | q1 | q0 |
| a | q1 | q1 | q2 |
| ab | q2 | q1 | q3 |
| abb | q3 | q3 | q3 |
2. Construct finite state automata (DFA) that contains with aab
Solution :
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with aa
q3 = string with aab
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with aa
q3 = string with aab
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
| f | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | ||
| ε | q0 | q1 | q0 |
| a | q1 | q2 | q0 |
| ab | q2 | q2 | q3 |
| abb | q3 | q3 | q3 |
3. Construct finite state automata (DFA) that contains with aba
Solution :
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with ab
q3 = string with aba
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with ab
q3 = string with aba
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
| f | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | ||
| ε | q0 | q1 | q0 |
| a | q1 | q1 | q2 |
| ab | q2 | q3 | q0 |
| abb | q3 | q3 | q3 |
4. Construct finite state automata (DFA) that contains with aabb
Solution :
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with aa
q3 = string with aabb
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
Σ: inputs = {a, b}
q0 = initial state
q1 = string with a
q2 = string with aa
q3 = string with aabb
Q: set of all states (q0, q1, q2, q3)
F: Final State
Transition Matrix
| f | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | ||
| ε | q0 | q1 | q0 |
| a | q1 | q2 | q0 |
| aa | q2 | q2 | q3 |
| aab | q3 | q1 | q4 |
| aabb | q4 | q4 | q4 |