Computer Notes, Programming codes, Hardware and Networking Tip, Entertainment, Biography, Internet Tip, Tech News, Latest Technology, YouTube,
Computer Fundamental
Hardware & Networking
Applications
Programming
Random Post
[random][newsticker]
May 2019
About RAM
Advantages of multiprocessing system
Associative memory
Binary Number System
CA
CA Notes
Change drive icon
change pendrive icon
Computer Abbreviation
Computer Architecture
Computer fundamental MCQ
Computer Generation
Computer generation computer notes
Computer MCQ
Computer Network MCQ
Computer Operator MCQ
Critical Section
Critical section in OS
Database connectivity in java
Deadlock avoidance
Deadlock detection algorithm
Deadlock Detection and Recovery
Deadlock detection method
Deadlock Handling
Deadlock in OS
Deadlock Prevention
Deadlock Recovery
define object and class
Define system cell
Descrete Structure
Device Driver
Device driver in computer
device driver in os
DFA
DFA contains with
DFA ends with
dfa examples
dijkstra's algorithm
Discrete Structure
Discrete Structure graph theory
Download JDBC Driver
Download MySql
Download PUBG
DS
DS Notes
FCFS Job Scheduling Algorithm
Finding shortest path
Finite Sate Automata
Flynn's Classifications
fragmentation in computer
fragmentation in harddisk
fragmentation in os
fragmented memory
Full form related to computer
Generations of operations
Generations of OS
Graph theory
ICT 1st semester notes
Instruction Address Modes
Java
java array declaration
java class and object example
Java Database connectivity example
java event handling example program
Java JDBC
Java JMenuBar
Java JSP program example
java notes
java program methods example
Java program to create class and object
java program to create methods
java program to print even number between any two numbers
Java programming
java programming notes
Java programs
Java question answer
java swing example
java swing program to calculate simple interest
Java Tutorials
JSP program
learn qbasic
Lekh
MCQ
MCQ Computer
MCQ Operating System
memory fragmentation
MICT 1st semester notes
mict 1st semester operating system notes
MICT first semester notes
Multiprocessing
mutex in os
Necessary conditions for deadlock
Number System
Operating System
Operating system notes
OS
OS Notes
OS Numeric
pattern printing program in qbasic
patterns in qbasic
Pipeline Hazards
Pipelining
Pipelining concept
prime or composite in qbasic
print patterns qbasic
print series in qbasic
Printing Series in qbasic
PUBG
PUBG Mobile
PUBG PC
PUBG Story
qbasic
qbasic code
qbasic for class 10
qbasic for class 8
qbasic for class 9
qbasic for school
QBASIC Pattern printing
qbasic pattern printing program
qbasic pattern printing programs
qbasic pattern types
qbasic patterns
qbasic programming tutorials
qbasic programs
qbasic sequence printing programs
qbasic tutorials
Race Condition in Operating system
reverse order in qbasic
RISC and CISC
RISC Pipeline
Scheduling algorithm
segmentation in operating system
segmentation in os
semaphore and mutex
Semaphore concept in os
Semaphore in os
semaphore in os notes
semaphore meaning
sequential programs in qbasic
series in qbasic
series printing programs in qbasic
shell in operating system
shell in os
shortest path
shortest path algorithm
simple interest program in java swing
System Bus
System Cell
Teach Blog
Tech Blog
Tech School
technical school
The Shell in Operating system
types of fragmentation
Types of Multiprocessor
types of operating system
Types of pipeline hazards
View Connected Wifi password
Virtual Memory
Virtual memory in OS
Von Neumann's architecture
What is associative memory?
what is class?
What is computer system?
What is Fragmentation?
What is jsp?
what is object?
What is process?
What is segmentation
What is System Cell
What is Thread?
what is virtual memory in computer
What is virtual memory?
पब्जी गेम
Concept of System Buses (Computer Architecture)
As we need a highway to travel from one place to another place. Similarly, the input and output of computer system also need a path to transmit data, information and control from one device to another device. The data transmit from input device to CPU, CPU to memory are common examples of system bus.
The path through which data and instruction flow is called bus of computer. It is a collection of wires, chips and slots inside the computer through which data and information are transmit from one part of computer to another.
Normally, Bus is available from 1 bit and above. The width of the bus determines how much data can moved at a time. Nowadays, PATA cables are replaced by SATA cables because of faster and small in size. These are also a way of transferring data and information from HDD to memory. Beside these cables there are numbers of buses inside the computer system (motherboard). There are three types of System bus they are :
1) Address Bus
The pathway through which transmit of address of memory location is called address bus. All types of memory devices have microscopic memory cells which are identified with unique humans known as memory address or memory locations. When the CPU reads data or instruction from memory or writes data to memory, it must specify the address of the memory location it is going to access. Unlike the other buses, the address bus always receive memory location from the CPU. There is one way flow in address bus.
2) Data Bus
The pathway (circuit / chips / wires / slots) through which transmit of data from one memory location to other is called Data Bus. When the CPU fetches data from memory, it first output the memory address on its address bus. Then the data bus. When writing data to memory, the CPU first outputs the address onto the address bus, then output the data onto the data bus. Memory the reads and stores the data to the proper location. The data flows in bidirectional way.
3) Control Bus
The pathway (circuit / chips / wires / slots) through which transmit of control signal to operate and control devices and software is called control bus. It is different from other two buses. The control bus is the collection of individual control signals for timing and controlling function sent by the control unit to other unit of the system. These signals indicate where data is to read or written, whether the CPU is accessing memory or an input/output device, and whether the I/O device or memory is ready to transfer data.
Generations of Computer (Computer note)
Rajkumar Lama
May 25, 2019
CA
,
Computer Architecture
,
Computer Generation
,
Computer generation computer notes
 Based on the period of development and the features incorporated the computer are classified into different generations from first generation to fifth generation computers.
Based on the period of development and the features incorporated the computer are classified into different generations from first generation to fifth generation computers.First Generation Computer
Computers which were made approximately between 1941 and 1955 A.D. are classified as the first generation computer. Vacuum Tube is the main technology, which was developed by Lee de forest in 1908 A.D.
- Technology : Vacuum Tube
- Processing Speed : processing speed was measured in millisecond
- I/O Devices : Punch card was used as input / output devices
- Compute Type : Computers were electron mechanical
- Memory : Vacuum tube was used as memory device
- Storage device : First punch card and later magnetic drum
- Operation Mode : Computer should be setup manually as there was no operating system
- Reliability and Accuracy : Not fully reliable and accurate
- Programming language : Machine level language
- Size and cost : Very large in size and expensive
- Availability : available to the military purpose and university research only
- Power and Heat : Consumed a lot of a electricity and emitted a lot of heat
- Portability : Computer were not portable
- Example : Mark I, ABC, ENIAC etc.
Second Generation Computer
Computer which were made approximately between 1955 to 1964 and having the transistor and diodes as main memory device are classified as the second generation computer. Transistor was designed by Walter Brattain, John Bardeen and William Sockley in 1947 A.D.
The main features of computer generation are as follows.
- Technology : Transistor (Main component)
- Processing Speed : Measured in Microsecond
- I/O Devices : punch card was used as input / output device
- Memory: Magnetic core memory is used as internal memory
- Storage device : Magnetic tape
- Operation mode : Should set up manually as there was not os.
- Reliability and Accuracy : More reliable and accurate then first generation computer.
- Programming language : Assembly and high Level language such as FORTRAN, ALGOL, COBOL etc.
- Size & cost : Smaller and less expensive then first generation
- Availability : Available for general purpose
- Power consumption and Heat : Power consumption and heat emission was less then first generation computer.
- Portable : Not portable
- IBM 1401, ICL 2950/10, IBM 1620 etc.
Third Generation Computer
The computers which were made approximately between 1964 to 1975 and having IC's technology as memory and processing devices are classified as third generation computer. The first IC was developed by Jack Kilby and Robot Noyce in 1985. Later Robert Noyce established Intel company.
- Technology : IC (Integrated Circuit)
- Processing Speed : Faster than previous generation computer
- I/O devices : Keyboard and Monitor
- Computer Type : Electronic
- Memory : Semiconductor memory (Primary memory)
- Storage Devices : Magnetic disk (Secondary memory)
- Operation Mode : Os was introduced for automatic and multi programming.
- Reliability and accuracy : Fully reliable and accurate
- Programming language : High level language for computer programming
- Size and cost : Smaller in size and less expensive then previous generations of computer
- Availability : Available for general purpose as well as for personal use.
- power consumption and heat emission : Power consumption and heat emission was less than previous generation computer
- Potable : Become portable computer because of development of Desktop and Laptop computer
- Example : IBM 360 Series, ICL 1900 etc, UNIVAC etc.
Fourth Generation Computer
The computer which were made approximately between 1975 to till now and having microprocessor as CPU and VLSI and ULSI technology in IC as memory device and classified as fourth generation computer.
- Microprocessor is a chip in which millions of components are integrated together in different layers.
- First commercial microprocessor was Intel 4004 made by Intel corporation in 1971 AD. It was 4 bit processor.
The main features of fourth generation computer are
- Technology : IC's and Microprocessor
- Processing speed : Faster then previous generations
- I/O devices : Fourth refined and invented various devices such as scanner, touch screen, printer etc.
- Computer type : Electronic
- Memory : Semiconductor memory with huge capacity
- Storage device : Magnetic and optical disk with large storage capacity for secondary storage device.
- Operation mode : Multi programming, multi processing, multimedia and distributed operating system become possible.
- Reliability and accuracy : Fully reliable and accurate
- Programming language : advance HLL and 4GL for application and database programming have been used.
- Size and cost : Smaller and less expensive then previous generations of computer
- Availability : General purpose as well as special purpose
- Power consumption and heat emission : It has been less then previous generation of computer
- Portable : Because portable off development of personal or Desktop computer, Laptop, Notebook, PDA etc.
- Example : Acer ASPIRE 5741, Apple MacBook Air, Dell Inspiration 1400 etc.
Fifth Generation Computer
Although the computer of this generation have not come yet in reality, but computers scientist are trying since 1990 A.d. It is said that the computer of this generation will use AI (Artificial Intelligence) and bio-chips as memory devices so that they can think and decide this like a human being.
Features of fifth generation computer are as follows
- They will be super conductor memory like bio-chips that the speed will be very fast.
- The computer will be intelligent and knowledge base because of AI.
- Instead of HLL, natural languages will be used such as English, Nepali, Hindi for giving instruction
- this computer will have power of seance, logic and decision making capacity
Micro Operation (Computer Architecture)

In computer CPU the micro-operations are
detailed low-level instructions which is used in some designs to implement
complex machine instructions. Usually, micro-operations perform basic
operations on data stored in one or more register, including transferring data
between registers or between registers and external buses of the CPU and
performing arithmetic or logical operations on registers. The execution of
micro-operations is performed under control of the CPU’s control unit which decides
on their execution while performing various optimizations such as reordering,
fusion and caching of the operations.
The operations executed on data stored
in registers are called micro-operations. A micro-operation is an elementary
operation performed on the information stored in one or more registers. The
functions built into registers are examples of micro operations, They are
Shift, Load, Clear, Increment, add, subtract, complement, and, or, xor etc ..
There are Four Types of Micro Operations
1.
Register transfer micro-operations
2.
Arithmetic micro-operations
3.
Logic micro-operations
4.
Shift micro operations
1) Register transfer micro operation
Register transfer language is a kind of intermediate
representation (IR) that is very close to assembly language, such as that which
is used in a compiler. It is used to describe data flow at the register
transfer level of an architecture. It is a convenient tool for describing the internal
organization of digital computers in concise and precise manner. These types of
micro operations are used to transfer binary information from one register to
another. Often the names indicate function:
- MAR – Memory Address Register
- PC - Program Counter
- IR - Instruction Register
In this case
the contents of register R1 are copied (loaded) into register R2
2) Arithmetic Micro-Operations
These
micro-operations are used to perform some arithmetic operations on numeric data
stored in the registers. A micro operation is an elementary operation performed
on the information stored in one or more registers. The micro operation in
digital computers is of 4 types: Addition,
Subtraction, Increment, and Decrement
- Addition:-
R1 = A + B
R3 = R1 + R2
- Subtraction: -
R1 = R2 – R3
Subtraction operation also can be performed on 2’s complement R = R1 + R2’ + 1
- Increment:-
R1 = R1 + 1, R2 = R2 + 1
- Decrement:-
R1 = R1 – 1, R2 = R2 – 1
3) Logic Micro-Operations
These micro
operations are used to perform bit style operations or manipulations on non-numeric
data. In computer CPU, micro-operations are the functional or atomic
operations of a processor. Logic micro operations are bit-wise operations,
i.e., they work on the individual bits of data. These are useful for bit
manipulations on binary data and also useful for making logical decisions
based on the bit value.
R1 = R1 XOR
R2
R2 = R3 AND
R4
4) Shift Micro-Operations
These are used for serial transfer of data. That
means we can shift the contents of the register to the left or right. In the shift
left operation the serial input transfers a bit to the right most position
and vice versa.
There are three types of shifts as follows:
a) Logical Shift
It transfers 0 through the serial input. The symbol "shl" is used for logical shift left and "shr" is used for logical shift right.
R1 ← she R1
R1 ← she R1
The register symbol must be same on both sides of arrows.
b) Circular Shift
This circulates or rotates the bits of register around the two ends without any loss of data or contents. In this, the serial output of the shift register is connected to its serial input. "cil" and "cir" is used for circular shift left and right respectively.
R1 = cir R1
R2 = cil R2
c) Arithmetic Shift
This shifts a signed binary number to left or
right. An arithmetic shift left multiplies a signed binary number by 2
and shift left divides the number by 2. Arithmetic shift micro-operation
leaves the sign bit unchanged because the signed number remains same when it is
multiplied or divided by 2.
R ← ashl R (arithmetic shift left R (register))
R ← ashr R
(arithmetic shift right R (register))
RISC and CISC Processors

RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) Processor
RISC is known as Reduced instruction Set Computer. It is a type of microprocessor that has limited number of instructions. It can execute it's instructions very fast because instructions are very small and simple.
RISC chips require fewer transistors which make them cheaper to design and produce. Most Instructions complete in one cycle, which allows the processor to handle many instructions at same time. In this type of processor, instructions are register based and data transfer takes place from register to register.
Features of RISC- Simple and small instruction
- Instruction come under size of one word
- Instruction take single clock cycle to get executed
- Simple addressing modes
- Less data types
- Pipeline can be achieved
- More number of general purpose register
CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) Processor
CISC is known as Complex Instruction Set Computer. It was first developed by Intel corporation. It contains large number of complex instructions. In this processor instructions are not register based and instructions cannot be completed in one machine cycle. Data transform is from memory to memory. Micro programmed control unit is found in CISC. It also have variable instruction format.
Features of CISC
- Complex instruction, hence complex instruction decoding
- Instruction may take more than single clock cycle to get executed
- Instruction are larger than one word size
- Complex addressing mode
- More data types
Difference Between CISC and RISC
| RISC | CISC |
|---|---|
|
|
How to change drive icon of Pendrive
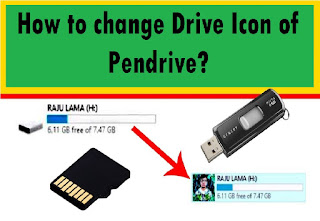
Pendrive is one of our must important storage device, where we store our documents or data. Normally, when we pluck our Pendrive to our PC, it displayed default icon every time. We can put our own photo or icon instead of default icon. To change the icon of removable disk / prndrive follow the following steps.
Before following the steps we should have our own icon/photo and Pendrive.
Step 1: Right click on the picture or icon which you want to set as drive icon and click on Edit.
Step 6: Paste it in Removable Drive (Pendrive)
Step 7: Remove your Removable Drive (Pendrive) and insert again. Your drive icon will be changed.
Step 1: Right click on the picture or icon which you want to set as drive icon and click on Edit.
Step 2: Your picture will be open in Paint program. Crop the picture using select tool and crop tool.
Step 3: Click on File > click on Save as > type the picture name (e.g myicon) > click on save as type > and choose 24-bit Bitmap (*.bmp; *.dlb) > finally choose your location and click on save.
Step 4: Now open Notepad program (press Win+R key >type : notepad in press enter key) and type the following code, and save it with autorun.inf file name.
[autorun]
icon = myicon.bmp
Step 5: Copy the picture file (myicon.bmp) and autorun.inf file.
Step 6: Paste it in Removable Drive (Pendrive)
Step 7: Remove your Removable Drive (Pendrive) and insert again. Your drive icon will be changed.
It's look like unique then others, Isn't it? (You can hide myicon.bmp and autorun.inf file)
Video Tutorial
Instruction Address Modes (CA Notes)
Rajkumar Lama
May 15, 2019
CA
,
Computer Architecture
,
Instruction Address Modes
,
MICT first semester notes
It specifies a rule for interpreting or modifying the address field of the instruction before the operand is actually referenced. It helps for


- Providing programming flexibility to the uses.
- Using the bits in the address field of instruction efficiently
Types of Addressing Modes
1) Implied Addressing Mode
- Address of operands are specified implicit in the definition of instruction.
- It does not need to specify address of instruction
- Example : Add x; Add y;
2) Immediate Addressing Mode:
- Instead of specifying the address of operand itself is specified in the instruction.
- No need to specify address in the instruction.
- However, operand itself need to be specified.
- Sometimes, require more bits to be address.
- Fast to acquire an operand
3) Register Addressing Mode
- Address specified in the instruction is the address of register.
- The instruction has the address of the Register where the operand is stored.
- Shorter address then memory address.
- Shorter instructions and faster instruction fetch
- Saving address field to access to the operands
- It has very limited address space
4) Register Indicate Addressing Mode
- In this mode, the instruction specifies the register whose contents give us the address of operand which is in memory. Thus the register contains the address of operand rather than the operand itself.
- Instruction specifies a register which contains the memory address of operand
- Saving instruction bits since register address is shorter than memory address
- Slower then register and memory addressing
- Example: EA = contend of R
5) Auto increment or Auto Decrement address mode
- In this mode the register is increment or decremented after or before its value is used.
- Instruction specifies the memory address which can be used directly to access the memory.
- Faster then the memory addressing mode
- Too many bits are needed to specify the address for a physical memory space.
- Example: EA = IR (Address)
6) Direct Addressing Mode
- In this mode, effective address of operand is present in instruction itself.
- Single memory reference to access data
- No additional calculation to find the effective address of the operand
- For Example: Add R1, 4000, In this the 4000 is effective address of operand.
7) Indirect Addressing Mode
- The address field of an instruction specifies the address of a memory location that contains the address of the operand.
- When the abbreviated address is used large physical memory can be addressed with the relatively small number of bits.
- Slow acquire operand because of an additional memory access.
- Example: EA = M[IR )address)]
The address field of instruction specifies the part of the address which can be used along with a designed register to calculate the address of the operand.
- Address field of the instruction is short
- Large physical memory can be accessed with a small number of address bits.
- There are three addressing mode
There are three different other register addressing mode:
- PC Relative addressing Mode (EA = IX + IR(address))
- Indexed Addressing Mode (EA = IX + IR (address)) / [IX is indexed register]
- Base Register Addressing Mode (EA = A + (R)
Number System (Binary Calculation)

A number system is a system for expressing numbers that is mathematical notation used for manipulating other countable things. The numbers are represented in different based system in different situation. The decimal number system is used for human counting but not role in machines. Binary numbers are used in modern digital devices. Octal and Hexadecimal number system are just packages of 4 binary bits. In computer science we have to study four number systems. They are
- Binary Number System (0, 1) / Base or radix = 2
- Octal Number System (0 to 7) Base or radix = 8
- Decimal Number System (0 to 9) Base or radix = 10
- Hexadecimal Number System (0 to 9 and A to F) Base or radix = 16
The following table shows the number system equivalent to one another.
Binary
|
Octal
|
Decimal
|
Hexadecimal
|
0000
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0001
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0010
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
0011
|
3
|
3
|
3
|
0100
|
4
|
4
|
4
|
0101
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
0110
|
6
|
6
|
6
|
0111
|
7
|
7
|
7
|
1000
|
10
|
8
|
8
|
1001
|
11
|
9
|
9
|
1010
|
12
|
10
|
A
|
1011
|
13
|
11
|
B
|
1100
|
14
|
12
|
C
|
1101
|
15
|
13
|
D
|
1110
|
16
|
14
|
E
|
1111
|
17
|
15
|
F
|
- Binary Number System : Any number having base or radix 2 and the number consists 0 and 1 only are called binary number system. E.g: 11102, 10012, 1110012
- Decimal Number System: Any number having base or radix 8 and the number consists 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 are called octal number system. E.g: 5638, 12358, 57368
- Decimal Number System: Any number having base or radix 10 and the numbers consists 0, 1, 2, ........ 9 are called decimal number system. E.g : 19610,
25810, 123610
- Hexadecimal Number System : Any number having base or radix 16 and the number consists 0, 1, 2, 3, ...... 9 and character consist A, B, C, D, E and F are called hexadecimal number system. Where A=10, B=11, C=13, D=14, E=15 and F=15. E.g : 25A16, 156B16, 9D16
Binary Calculation
The modern digital computer system performs every calculations in the form of binary format. They present 0 or 1, on or off, presence and absent. It represents the status.
Binary Addition:
Binary addition is performed in a similar way to decimal addition.
Binary Addition
|
||
X
|
Y
|
X+Y
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
10 (with a carry of 1)
|
Example: a) Add 110102 + 10012 b) 111102 + 111012
Binary Subtraction:
Binary subtraction, similar method is adopted as in decimal system.
Binary Subtraction
|
||
X
|
Y
|
X-Y
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
1 (with a borrow of 1)
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
Example : a) 10010 - 1011 b) 1101101 - 111101
Binary Multiplication
Binary multiplication is easier since there is no number as "carry" value. The following rule is adopted in binary multiplication. The values are added column wise as in binary addition.
Binary Multiplication
|
||
X
|
Y
|
X*Y
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
Example: a) 11101 x 111 b) 100011 x 110
Binary Division
Binary Division is similar to decimal division. If a number cannot be divided, put 0 to the quotient. If division is possible put 1 to the quotient. Multiplication and subtraction is as discussed in binary multiplication and binary subtraction.
Example: a) Divide 1011 by 11 b) 111 by 11
For Practice :
- Binary Addition
- 1011 + 11
- 11111 + 10101
- 11100 + 10111
- Binary Subtraction
- 1011 - 1000
- 101010 - 11001
- 11011 - 1010
- Binary Multiplication
- 1110 x 110
- 1101 x 111
- 11101 x 1011
- Binary Division
- 10011 by 110
- 11100 by 1110
- 1110 by 110
MKRdezign
Powered by Blogger.












